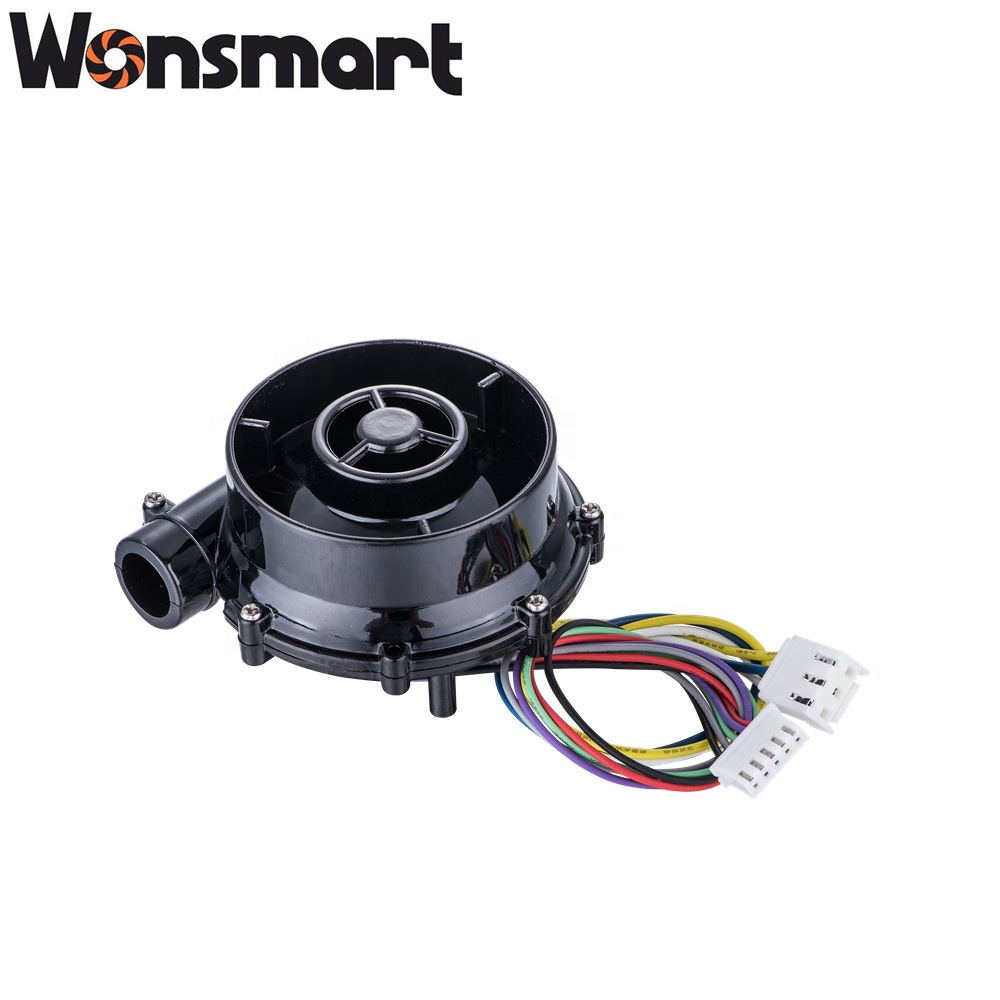
Best-Selling 12v Dc Electric Motor - 24 Vdc mini centrifugal air blower fan – Wonsmart
Best-Selling 12v Dc Electric Motor - 24 Vdc mini centrifugal air blower fan – Wonsmart Detail:
Blower Features
Brand name: Wonsmart
High pressure with dc brushless motor
Blower type: Centrifugal fan
Voltage: 24vdc
Bearing: NMB ball bearing
Type: Centrifugal Fan
Applicable Industries: Manufacturing Plant
Electric Current Type: DC
Blade Material: plastic
Mounting: Ceiling Fan
Place of Origin:Zhejiang, China
Voltage:24VDC
Certification: ce, RoHS, ETL
Warranty: 1 Year
After-sales Service Provided: Online support
Life time(MTTF): >20,000hours (under 25 degree C)
Weight: 80 grams
Housing material:PC
Unit size: D70mm *H37mm
Motor type:Three Phase DC Brushless Motor
Outlet diameter: OD17mm ID12mm
Controller: external
Static pressure: 6.8kPa
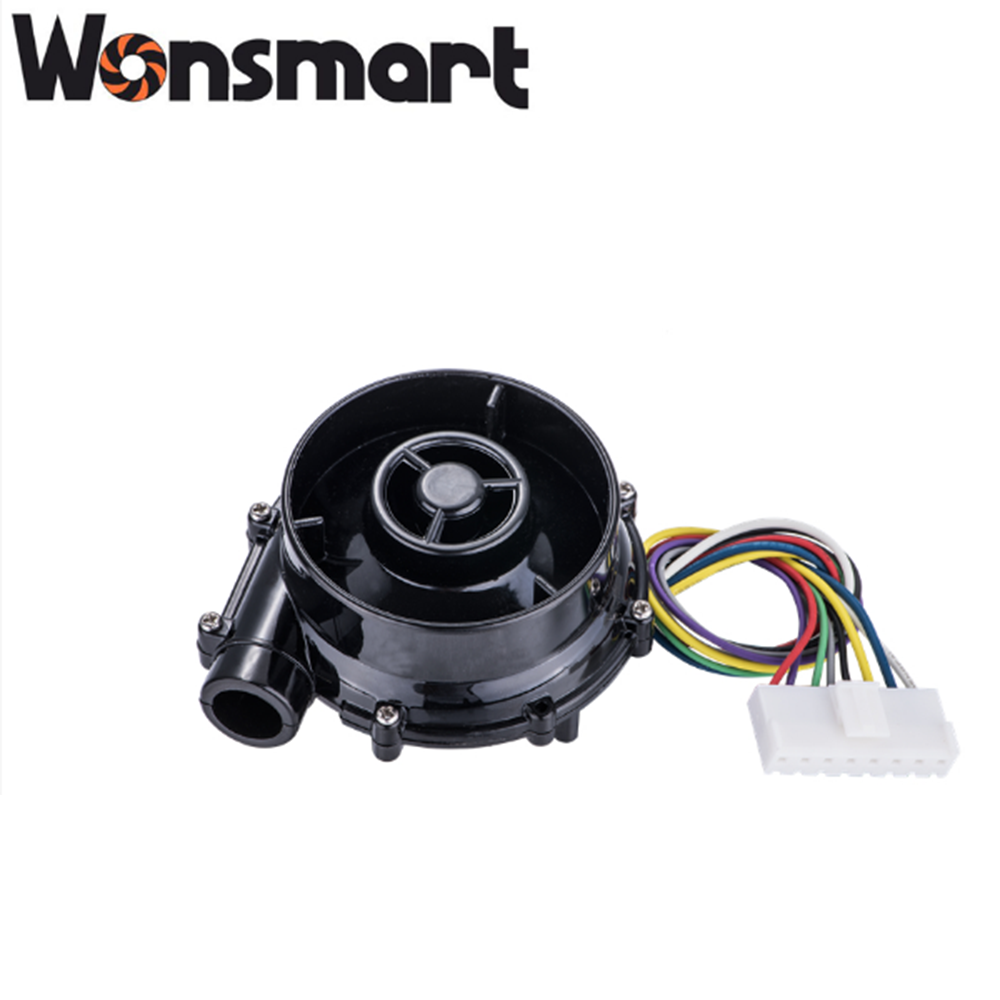
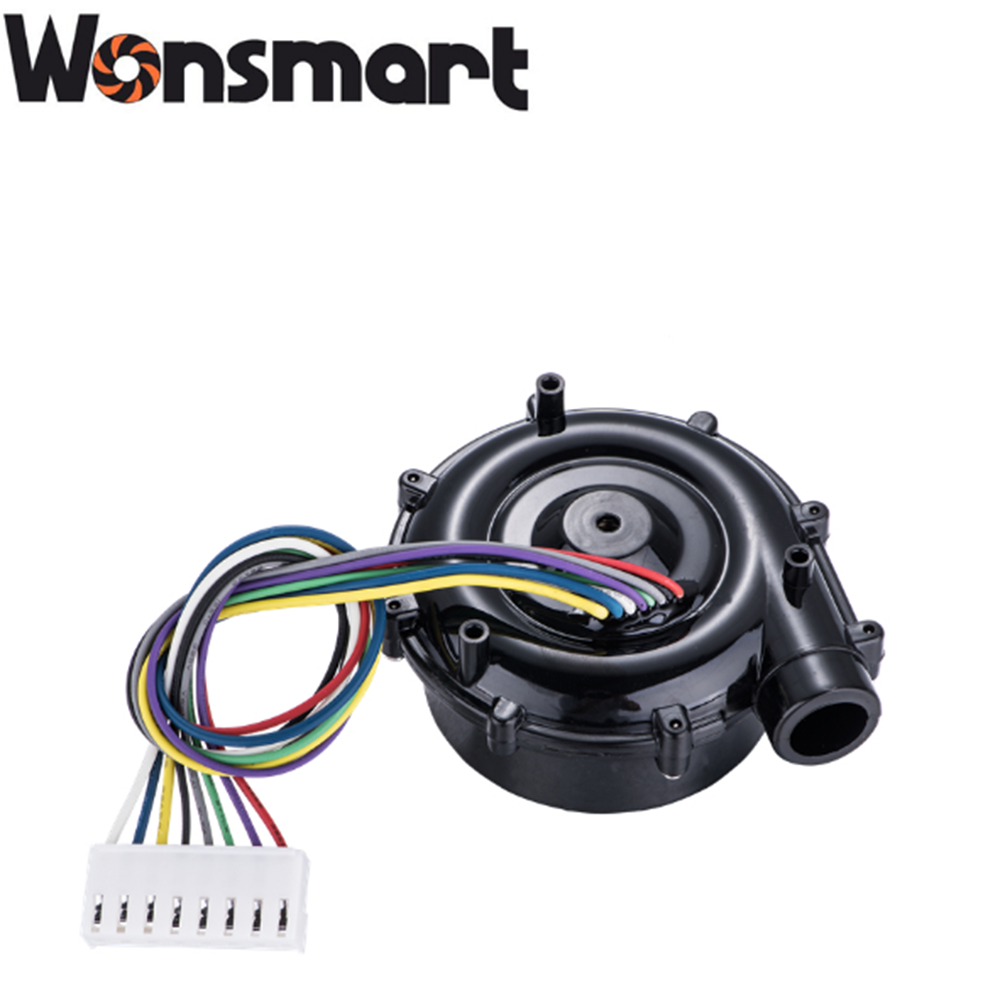


Drawing
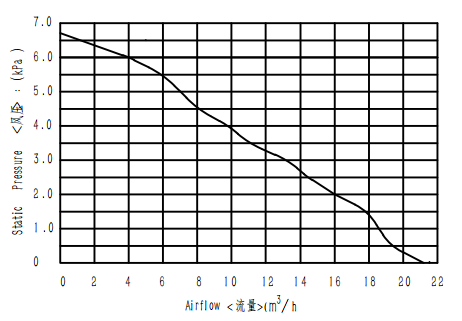
Blower Performance
WS7040-24-V200 blower can reach maximum 22m3/h airflow at 0 kpa pressure and maximum 6.8kpa static pressure. It has maximum output air power when this blower run at 3kPa resistance if we set 100% PWM. It has maximum efficiency when this blower run at 5.5kPa resistance if we set 100% PWM. Other load point performance refer to below P-Q curve:
DC Brushless Blower Advantage
(1) WS7040-24-V200 blower is with brushless motors and NMB ball bearings inside which indicates very long life time; MTTF of this blower can reach more than 20,000 hours at 20 degree C environmental temperature.
(2) This blower needs no maintence
(3) This blower drived by a brushless motor controller have many different control functions such as speed regulation,speed pulse output,fast acceleration, brake etc.it can be controlled by intelligent machine and equipment easily.
(4) Drived by brushless motor driver the blower will have over current, under/over voltage,stall protections.
Applications
This blower can be widely used onto air cushion machine, CPAP machine, SMD soldering rework station.
How to Use the Blower Correctly

FAQ
Q: Customer: May I use this blower for Medical device?
A: Yes, this is one blower of our company which can be used on Cpap and ventilator.
Q: What’s is the maxmum air pressure?
A: As it shown in the drawing, the maxmum air pressure is 6.5 Kpa.
The centrifugal fan uses the centrifugal power supplied from the rotation of impellers to increase the kinetic energy of air/gases. When the impellers rotate, the gas particles near the impellers are thrown off from the impellers, then move into the fan casing. As a result, the kinetic energy of gas is measured as pressure because of the system resistance offered by the casing and duct. The gas is then guided to the exit via outlet ducts. After the gas is thrown-off, the gas pressure in the middle region of the impellers decreases. The gas from the impeller eye rushes into normalize this. This cycle repeats and therefore the gas can be continuously transferred.
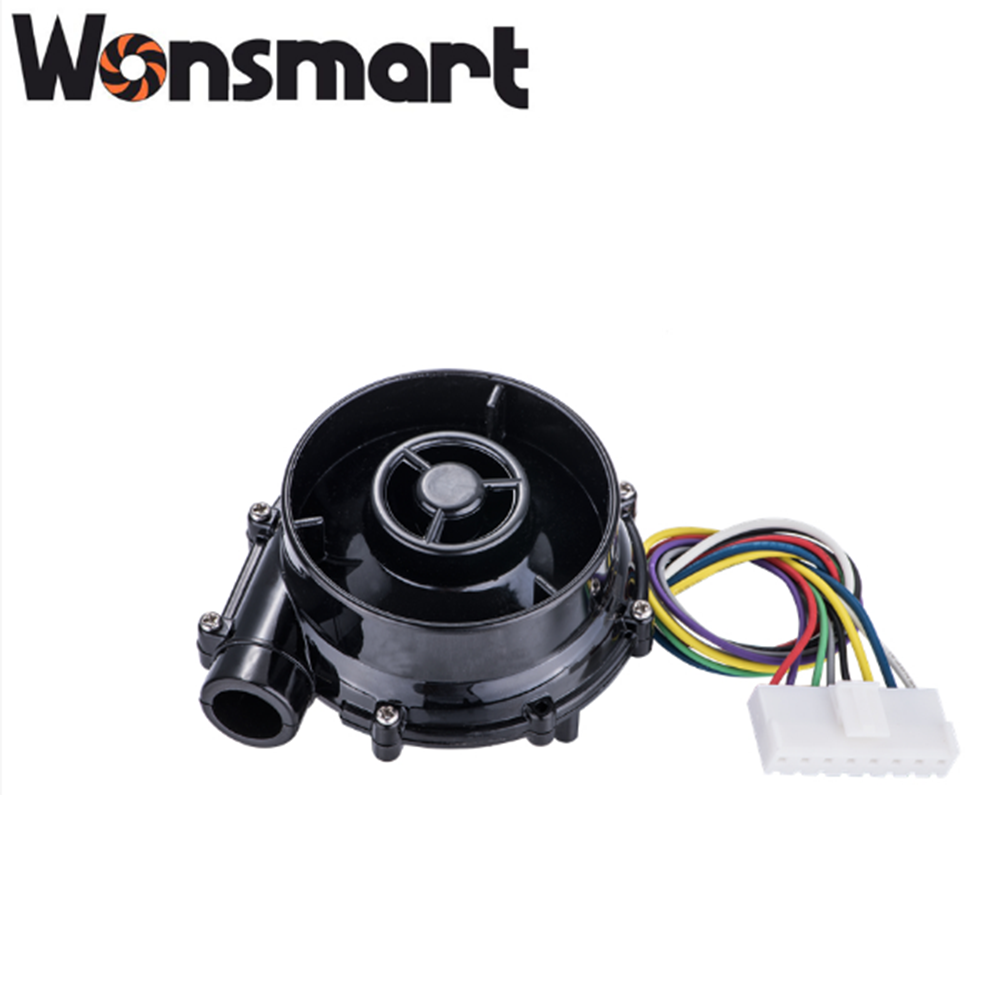
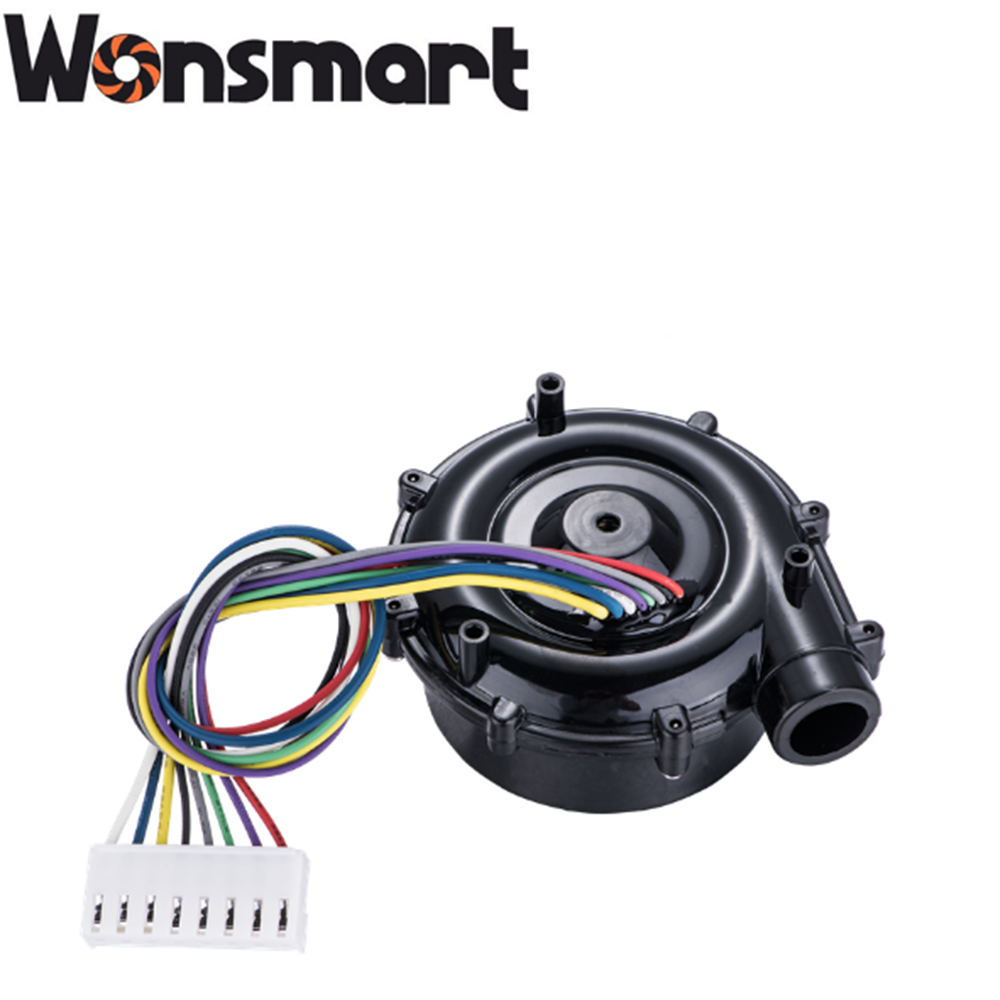
Product detail pictures:


Related Product Guide:
It truly is a great way to improve our merchandise and repair. Our mission should be to create imaginative products to prospects with a excellent knowledge for Best-Selling 12v Dc Electric Motor - 24 Vdc mini centrifugal air blower fan – Wonsmart , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Greek, Munich, Mexico, With the development of the society and economy, our company will continue the "loyalty, dedication, efficiency, innovation" spirit of enterprise, and we will always adhere to the management idea of "would rather lose gold, do not lose customers heart". We will serve the domestic and foreign businessmen with sincere dedication, and let us create bright future together with you!
The customer service staff's answer is very meticulous, the most important is that the product quality is very good, and packaged carefully, shipped quickly!






